How Do Forex Brokers Make Their Money?

Like it or not, Forex brokers are an integral part of any trader’s life. That’s why it’s important to understand how they operate, how they make their money and how to protect against bad broker practices such as stop-hunting.
In the following lines, we’ll dig deeper into what Forex brokers are, what their main types are and how they make their profit. We’ll also explain whether Forex brokers trade against their traders, and if so, how to identify such a broker.
What are Forex Brokers?
A Forex broker is a company that provides traders with access to the foreign exchange market. In essence, Forex brokers are a middleman between Forex traders and the market. They offer a range of services, including trading platforms, which are used to buy and sell foreign currencies.
Once you send an order through your trading platform, your broker tries to match the order either with its internal pool of traders or forwards it to external liquidity providers to find the best opposite order. Each time you place a sell order, it has to be matched with a corresponding buy order, and vice-versa.
Forex brokers, also known as retail Forex brokers, account for a relatively small amount of the daily Forex market turnover. According to a BIS research, retail Forex makes up around 5% of the total $5 trillion market.
[adinserter block=”4″]
Main Types of Brokers
There are two main types of Forex brokers: dealing desk (DD) brokers and no dealing desk (NDD) brokers. NDD brokers can be further divided into STP, ECN and ECN+STP brokers. All mentioned types of brokers have their own advantages and disadvantages, which are explained below.
- Dealing Desk
Dealing desk or DD brokers, also called market makers, provide liquidity to their clients and create the market for them. They’re called market makers because they’re the main source of liquidity for their traders. Most of the time, dealing desk brokers take the opposite side of their client’s position. If you’re selling, they’re buying from you, and vice-versa.
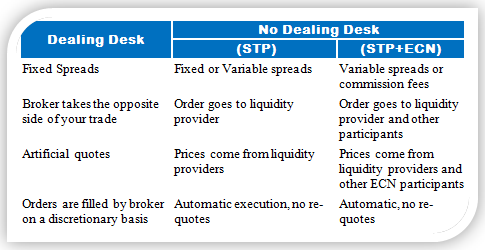
Since dealing desk brokers create the market for their clients, they have the full discretion to set both bid and ask prices of a currency pair. Dealing desk brokers don’t have necessarily to provide interbank rates, but the large competition among brokers makes sure that the offered rates don’t differ much from interbank rates. Also, dealing desk brokers often offer fixed spreads.
- No Dealing Desk
No dealing desk brokers don’t pass their clients’ orders through a dealing desk.
They simply act as a middleman between their clients and other liquidity provider, either internal or external ones. Once you place a trade with a no dealing desk broker, the broker will first try to match your order with its internal liquidity pool. If there are no matching orders, the broker will forward your order to external liquidity providers, which can include banks, mutual funds, hedge funds, other brokers etc.
Since no dealing desk brokers don’t know at which price your order will be filled, they usually offer variable spreads with a small markup that compensates them for their services.
The following graphic summarises the main difference between DD and NDD brokers pretty well.
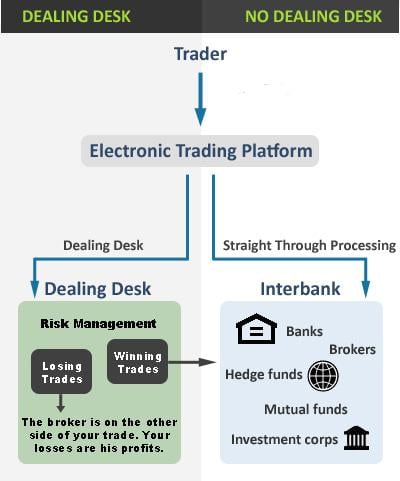
No dealing desk brokers are further divided into STPs, ECNs and a combination of both (ECN+STP.)
-
- STP – Straight Through Processing (STP) brokers, as their name suggests, forward your order immediately to external liquidity providers which have access to the interbank market. Once they find the best matching order, they’ll add their spread and fill your order at the external provider’s price + the broker’s spread.
-
- ECN – Electronic Communication Network (ECN) brokers are true NDD brokers as they represent the bridge between retail traders and the interbank market. ECN brokers simply provide a sophisticated network that connects various market participants together, such as hedge funds, banks, other brokers and retail traders. All mentioned market participants trade directly with each other, and the ECN broker charges a small commission for its services.
-
- ECN+STP – Finally, some brokers offer a combination of STP and ECN services. Those brokers are called ECN+STP brokers.
Here’s a table to make the difference between the main types of brokers crystal clear.
How do Forex Brokers Make Money
Now that you know what Forex brokers are and their main types, let’s take a look at how they make their money. In essence, the major source of a broker’s income is the spread, followed by other sources of revenue such as commissions/fees, trading platforms and additional services.
- Spread – The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices of currency pairs. Whenever you go long on a currency pair, you’ll get the ask price. Similarly, if you decide to close your long position or want to go short on a currency pair, you’ll get the bid price. This difference between the bid and ask price is your broker’s profit. While some dealing desk brokers offer fixed spreads, most of the time spreads are variable and depend on the current market conditions. If there are important and unexpected news in the market, spreads can widen significantly and increase your trading costs. During normal market conditions, spreads tend to be quite low with most brokers, reaching around 1 pip for most major pairs. For day traders, the New York / London session overlap usually has the lowest spreads during the day.
- Commissions/Fees – Besides the spread, some brokers may also charge you a fixed commission or fee per trade. This is especially true with ECN brokers. However, commissions and fees tend to be quite low due to the high competition among Forex brokers. For example, a broker may charge you a $1 commission for a pre-specified lot size, such as 1 lot or 10 lots.
- Trading Platforms – The next major income for Forex brokers are trading platforms. While many brokers offer free in-house developed and third-party trading platforms, some of them may also charge you for additional features. If you’re a professional trader, you may look at the offer of Forex trading platforms provided by your broker and look for features that could help you in your daily trading. The main point to consider is that the offered feature increases your profitability and efficiency more than the cost of the service. Beginner traders, on the other hand, are likely fine with the range of features offered with free trading platforms.
- Additional Services – Finally, some brokers may offer additional paid services. For a small cost, you may get access to a larger range of tradable instruments, professional market research, trading signals and market depth information, to name a few.
Read: 6 Secret Practices to Watch Out For With Your Broker
Do All Brokers Make Money When You Lose?
As we already said earlier, some brokers take the opposite side of your trade as they are creating the market for you. Those brokers are called market makers. However, is it bad or illegal to be a market maker? Many traders have this question, so let’s cover it briefly.
Absolutely not! Market makers provide a service that people need.
There’s nothing wrong with being a market maker and taking the opposite side of a trader’s position. Market makers operate in the following way:
The transaction is fully legal. If you don’t agree with the offered exchange rate or transaction costs, you could always look for other brokers as this is a very competitive business. In addition, since most traders lose money while trading, a market maker doesn’t have to cheat you to make an extra profit from you.
Naturally, the problems start if a market maker decides to cheat you, either because of greed or fear. There is a certain conflict of interest involved in a market maker’s transaction, since your profits are the broker’s losses and vice versa.
Stop-hunting has been a very popular practice among market makers to make extra profits by artificially moving exchange rates to hit levels where a large number of stop-loss orders are placed. Fortunately, stop-hunting has become increasingly rare, especially among regulated market makers.
Being a market maker is simply a service that traders need and an operational type of Forex brokers – there’s nothing wrong in being an honest market maker per se.
Still, not all brokers make money when you lose. If you don’t like the idea of having a conflict of interest with your broker, you can always look for no-dealing desk brokers (STPs, ECNs or a combination of both.)
Read: What Subjective Benefits Should You Consider When Choosing a Broker?
What to Look for in a Forex Broker?
When opening a trading account with a Forex broker, there are certain things you need to pay attention to. We recommend you read our guide to choosing broker. We’ve also listed the most important below.
- Regulation – Always open an account with a regulated broker. Brokers are regulated and licensed by the country’s regulatory authority where they’re registered. Regulation ensures that the broker adheres to and enforces strong industry standards and that your funds are safe. Regulated brokers are happy to list their license number and regulatory authority on their website.
- Broker Type – Is the broker a dealing desk broker or a straight through processing / electronic communication network broker? You should know the type of your broker in advance to avoid any surprises down the road.
- Trading Costs – Trading costs are an important consideration when choosing a Forex broker. Due to the high competition, most brokers offer very tight spreads, especially on major pairs. Are the spreads fixed or variable? Are there any additional commissions or fees on opening trades? If you’re a day trader or scalper, trading costs can easily eat up a significant portion of your profits.
- Trading Tools – What trading tools does the broker offer? Besides free trading platforms (such as MetaTrader), most brokers offer free market analysis, market sentiment indicators and webinars nowadays.
- Customer Service – Last but not least, a broker should offer world-class customer support, reachable around the clock. If your trading platforms stops working or you are unable to open, manage or close trades, the first step you need to do is to contact your broker’s support.
Understanding your broker is a crucial part of your trading success
As a trader, you’ll be dealing with your Forex broker on a daily basis, paying transaction costs and contacting their customer support from time to time.
There are two types of brokers out there: Dealing desk broker (DD) and no dealing desk broker (NDD). Dealing desk brokers are also known as market makers, as they create the market for their clients and often take the opposite side of the trade. While there is nothing wrong with (regulated) market makers, some of them are notorious for bad broker practices such as stop-hunting.
If you don’t like the idea of being in a conflict of interest with your broker, you can look for no dealing desk broker which forward their clients’ orders to third-party liquidity providers. Whichever broker you choose, make sure to do your analysis and to pick the right broker for your trading needs.
[adinserter block=”4″]





